What Is 5G?
- 5G is the next generation of wireless communication systems, and it promises to bring about a new era of connectivity.
- It is set to provide faster data speeds, reduced latency, and increased bandwidth. This will allow for a slew of new applications and services, such as augmented reality and virtual reality.
- 5G will also be more reliable and secure than older generations of wireless communication systems.

An Overview of 5G Technical Parameters
- 5G is the next-generation of wireless communication systems that promises to deliver unprecedented speeds and bandwidth.
- 5G will operate in the millimeter wave spectrum, which is much higher than the frequencies used by 4G and 3G. This will allow it to carry more data and support faster speeds.
- 5G will also use a new modulation scheme called OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing), which is more efficient than the modulation schemes used by 4G and 3G. This will allow it to carry more data and support faster speeds.
- 5G has a number of advantages over older generation of wireless communication systems. It is faster, more efficient, and can support a greater number of devices.
- However, it also has a number of disadvantages, which include its high cost and limited coverage.
Advantages And Disadvantages Of 5G Compared To Older Generations Of Wireless Communication Systems
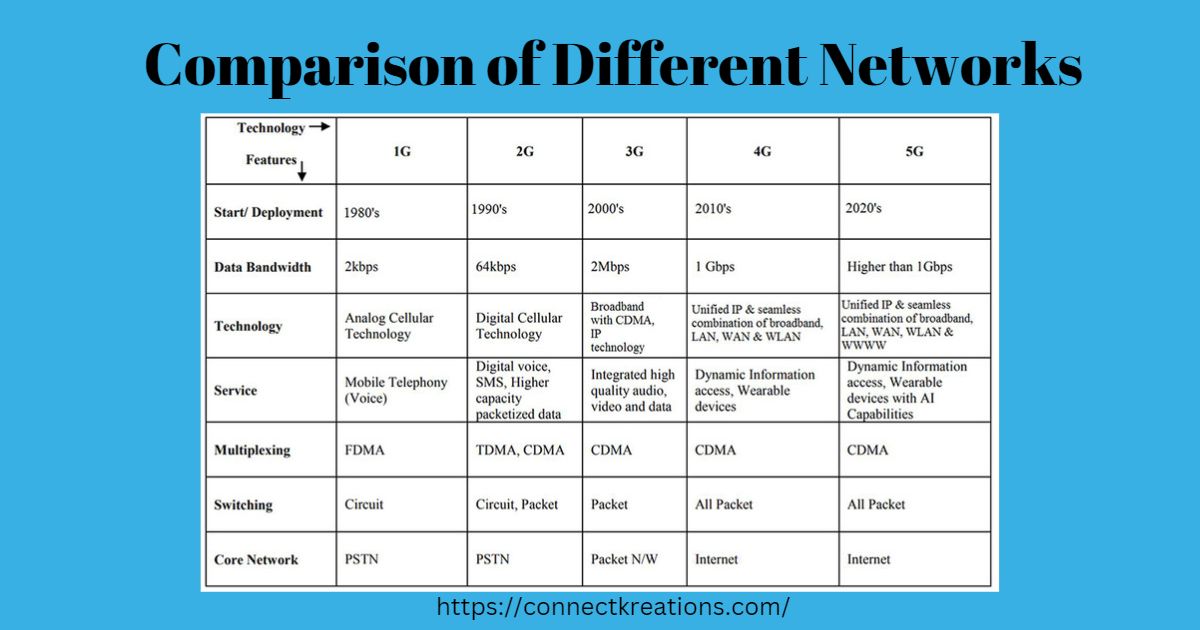
Fifth Generation Cellular Network Technology, or 5G, is an emerging standard developed and deployed for digital communications over wireless broadband networks. The highly anticipated Fifth Generation Mobile Telecommunications Technology, known as 5G, is expected to represent a quantum leap forward for mobile communications — promising blazingly faster upload speeds and the ability to share data in real-time.
Mobile technologies Fifth Generation (5G) is shaping up to be an excellent network for the web, bringing enhanced speeds, range, and reliability.
Successing the 4G LTE, LTE Advanced, and true 4G technologies, 5G promises to support current and future wireless communications applications, providing more reliable mobile connectivity and faster broadband Internet speeds. The faster speeds offered by 5G will enable new technology advances.
One benefit of this new fifth-generation wireless technology is more capacity will be available in data networks from companies like Verizon, T-Mobile, and Sprint. With more people being able to take advantage of the increased bandwidth, some may worry about the speeds they can expect to get on 5G networks.
Blazing-fast speeds are possible because more bandwidth allows for greater dedication of a network to each smart device. The network has a 20Gbps speed, which allows organizations to utilize it equally for services like automation, enhanced web conferences, and so on.
The 5G network will be capable of delivering download speeds of up to 20 times (4G at 200Mbps up to 10Gbps (5G)) and reduce latency (response times between devices). The next 5G generation will be capable of handling hundreds of billions of connections, and deliver transmission speeds of 10 Gbps with super-low latencies of 1ms. To reach high data speeds, a goal of
5G, 5G will utilize millimeter waves and a spectrum to transmit data. The millimeter waves in 5G allow very high-speed wireless communications, as well as offering an ultra-wideband capability for the next-generation mobile networks. Overall, 5G has some advantages over 4G because of new technologies, spectrum, and frequencies that it uses; higher speeds, lower latency, the ability for more connected devices, lower interference, and better efficiency.
Key advantages of 5G include higher communications speeds, reduced latency and thus greater flexibility in running remotely, larger number of connected devices, and ability to enable virtual networking or network slices, allowing more tailored access for personal needs.
Research is underway worldwide in order to develop a new technology that will play an extremely important role in successful deployment of fifth-generation mobile communications. The wireless technologies in future will deliver superfast, highly functional, highly secure mobile networks. The second generation of mobile communications systems introduced new digital technology to transmit over the air, namely the Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM).
Wireless Transmission technologies such as WiMax were introduced into the 4G systems in order to improve data rates and network performance. This will become a thing of the past, as those using a 5G network can surf the Web, download files, or even stream videos with blistering speeds. It is expected that IoTs billions of connected objects will produce data volumes well beyond the amount which can easily be processed and analyzed in the cloud, because of issues such as bandwidth limitations, network latency, and so on.
Potential Applications Of 5G
Designed to deliver the highest speeds and capacities, 5G has the potential to dramatically extend how data is moved, and it would allow a vast array of new applications and use cases, which would extend well beyond smartphones. The private 5Gnetwork to be built by Vodafone using equipment from Ericsson will allow a number of 5G industrial use cases, such as connecting workers with digital data and applications throughout an entire facility, increasing productivity while cutting costs, all in a far safer environment.
We anticipate that 5G will allow for new use cases in remote surveillance and visual inspection, autonomous operations in remote, large-scale environments like mines, connected vehicles, and much more.
Drones are becoming increasingly popular for multiple operations, from entertainment, video capture, access to healthcare and emergencies, intelligent freight solutions, security, surveillance, etc. A 5G network will offer a powerful backbone of high- speed wireless Internet connectivity to enable the operations of drones across a broad spectrum of applications.
A key characteristic of 5G network technologies is an increased level of connectivity amongst daily objects, enabled with faster Internet speeds, featuring smart facilities, indicating a coming revolution of the IoT driven 5G.
The 5G technology provides super-reliable, low-latency communications, as well as improved throughput. Overall, 5G (5G) wireless is expected to create various new applications, uses, and business cases as the technology is deployed. As 5G matures, companies that are serving the autonomous vehicle market by using 5G for private connectivity as a core part of their businesses will see new opportunities. Future industries will rely on advances in intelligent wireless technologies such as 5G and LTE to efficiently automate equipment, predictability, security, process monitoring, intelligent packaging, transportation, logistics, and power management. From evolving IoTs to groundbreaking advances in the way AI is used in the real world, many of the most exciting technology advances tomorrow will be dependent on 5G connectivity.
The smart home concept will leverage 5G networks to connect devices and monitor applications. Services will allow new types of pricing models and a far greater uptake of wireless connectivity across a wide range of IoT applications. Network slicing will allow wireless network connections to be tailored for particular uses or business cases, and can be sold as-a-service. To deliver some incredible 5G use cases, venues across the Cisco Sports & Entertainment portfolio will be able to take advantage of the mobility edge computing (MEC) capabilities of their 5G networks.
Fixed wireless access will be a boon to both home and enterprise uses, with a fifth-generation network that enables internet connectivity that can compete with fiber-to-the-premises, eliminating the need for landlines, and providing improved internet access to harder-to-access areas.
According to experts from the United Arab Emirates Technical Academy, 5G will increase applications for IoT as well as AI. According to the technology business research (TBR) Inc., it is expected that the network operators spend billions in 5G capital expenditures till 2030, though how 5G (Fifth Generation Wireless) services would bring a return on this investment is unclear.
Benefits And Challenges For Businesses With 5G
With faster speeds, lower latencies, and better connectivity, the benefits and challenges 5G presents to businesses–and the innovations that 5G brings–will be virtually endless. In terms of connectivity, the Internet of Things is expected to expand exponentially, relying on 5G networks to service billions of devices all at once. With 5G networks increasing speed and data capacity, your company can cope with the sheer volume of data and network connections IoT devices will bring.
Like Wi-Fi 6, 5G will also more effectively distribute network resources, providing connections for more devices from one source. Mobile phone users can expect faster connections with greater bandwidth once they opt for 5G networks. Increased reliability: In addition to increased speeds, 5G technology will provide greater reliability and lower data loss to consumers and businesses using enterprise applications. The improvements offered with 5G will provide businesses with lightning-fast data transmission speeds and enhanced network reliability.
With increased speeds and robust mobility offered by 5G, small-to-medium-sized businesses will be able to take advantage of new opportunities within their industries, while better meeting customer demands. Mobility, connectivity, and wireless productivity have an infinite amount of benefits for businesses of all sizes, but smaller businesses, especially, will be able to increase productivity and lower costs, which in the long term, will be good for their bottom lines. With any new wireless generation deployment, such as 5G, benefits will increase over time as networks increase their reach and technologies improve.
These benefits could enhance service delivery with enhanced visual experiences, faster response times, and better use of devices, as well as enable smaller, more portable devices for novel applications. More concretely, 5G means that you can connect more devices, enjoy faster, more reliable connections, strengthen security, and enhance the mobility of your company in todays world focused on remote work. To take advantage of 5G networks, users will need smart devices that support 5G.
Much of the deployment of 5G cell technologies will occur on top of existing 3G and 4G spectrum, which allows for backwards compatibility with older devices. Like earlier mobile networks, 5G networks will typically be deployed in denser locations, where hundreds of devices will have to be connected to them. To enable connectivity without deployment, maintenance, and power costs going through the roof, 5G will seamlessly link networks of embedded sensors within smart devices at a low latency, as well as being able to reduce data rates, energy, and mobility in order to deliver lower-cost solutions.
While carriers are continuing to open up more of their allocated spectrum for 5G at higher speeds, the performance and lower latency that is prized by 5G cell technologies will mostly be found in millimeter-wave deployments, which will be much more limited in range reflecting the issue of proximity. Companies need to look beyond 5Gs cell-technology advantages and into the limitations of 5G when planning wireless networks going forward.
What Does This Mean For Our Future 5G?
For Dejero, 5G is just the latest ingredient in our mix-and-match formula, joining 4G, satellite, WiFi, and a broadband connection. The increased reliability and lower latency achieved from mixing networks with 5G will further accelerate workflows, streamline operations, and open up new use cases for our customers. The biggest improvements to speed and latency will occur as service providers deploy stand-alone 5G networks, in which the superfast 5G is used by both the core and the radio networks.
Needless to say, this new technology opens up a whole new set of opportunities for telecom providers. It is the wave of wireless technologies which is beyond 4G networks which are in use today. The technologies needed to fuel a new 5G network are bound to transform how mobile devices are used, and also how they are capable.
The 5G cell network will also redefine consumer electronics experiences, unleashing a new era in mobile video, and driving huge increases in IoT and smart devices, along with enhanced AR/VR capabilities. This technology has the potential not only to dramatically reduce the total cost of infrastructure, but it may open doors for an array of new geo-information applications. For some, a 5G cell phone network promises nothing more than improved cell phone capabilities, providing enhanced broadband capacity, and increasing mobile data speeds.
Overall, fifth-generation wireless (5G) is expected to create various new applications, uses, and business cases as the technology is deployed. With its increased data transmission speeds, 5G ultra-wideband will ultimately enable the connectivity of even more technologies, making possible an Internet of Things at a truly massive scale. The higher speeds, lower latency, and greater capacity will be key in enabling us to connect to each other far more than we have in the past, powering Internet of Things devices, while also enabling revolutionary applications in industries such as broadcasting and media production.
The entire purpose of a new 5G network is to enable the consumption of more devices at faster speeds than ever, because of that purpose, energy use is sure to rise around the world. The speeds you will receive will depend on what spectrum bands an operator is running the superfast 5G on, and how much the operator has invested in new masts and transmitters.
It is new radio technology, but you may not initially notice much faster speeds, as the reason for this is that five-G is probably being used initially by network operators as a way of increasing capacity in existing four-G base networks, in order to provide customers with a more stable service.
With those improvements, plus the use of millimeter-wave spectrum and the deployment of an extensive fiber network, Verizon was able to roll out Verizon 5G Ultra Wideband–a technology we anticipate will disrupt the industry and provide an immediate impact to customers–faster and more effectively. When you picture the future powered by 5G, you think connected factory devices talking to one another, mobile Internet connecting multiple devices simultaneously, various vehicles communicating with the roads they are traveling along, and accessing information at an unprecedented rate.
Architecture Of 5G
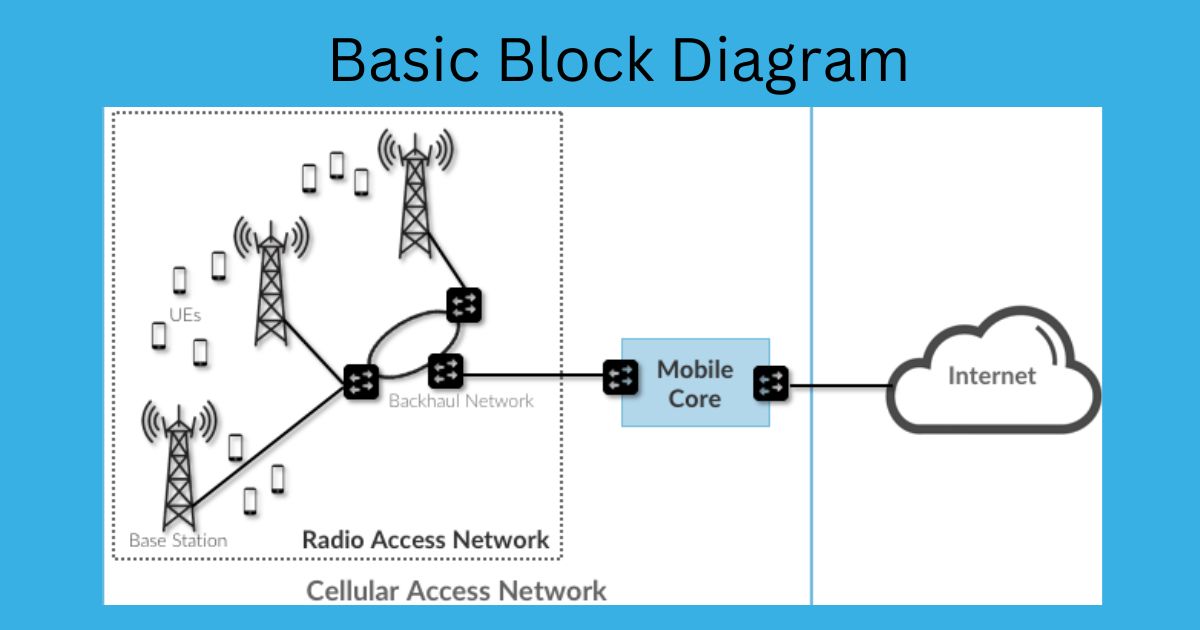
Service-based architecture is applied for control plane, whereas the reference point architecture is used for user plane inthe 5G core network. The 3GPP defines Service Based Architecture (SBA), in which control plane functions and shared data stores for a 5G network are delivered via a set of interconnected network functions (NFs), each of which has permissions to access the services of the others. The core network architecture for 5G leverages a cloud-aware, Service-Based Architecture (SBA) spanning across all functions and interactions in 5G, including authentication, security, session management, and aggregation of end-device traffic.
The new architecture for 5Gc is built upon the so-called service-based architecture (SBA) which brings its networking principles and a cloud-native design approach. The 5G Core Network architecture further highlights NFV as a built-in design concept, with virtualized software functions able to be deployed using MEC infrastructure, which is core to 5Gs architectural principles.
The 5G core network supports the virtualization of software functions for use with NFVI in 5G network designs, including the MEC infrastructure. More flexible architectures using SDN (software defined networking) and Network Functions Virtualization (NFV). Virtualized networking components, which decouple hardware and software, make for more open architecture, including RAN.
Developers designed 5G wireless networking architecture from the ground up, decoupling network functions by type of service. The 5G core is entirely software-based and cloud-native, which allows for higher deployment elasticity, as well as having a flexible, similar-to-cloud infrastructure. The wireless network architecture of 5G is service-oriented, modular, reusable, and a self-contained architecture which is capable of providing high-speed, ultra-low-latency networks.
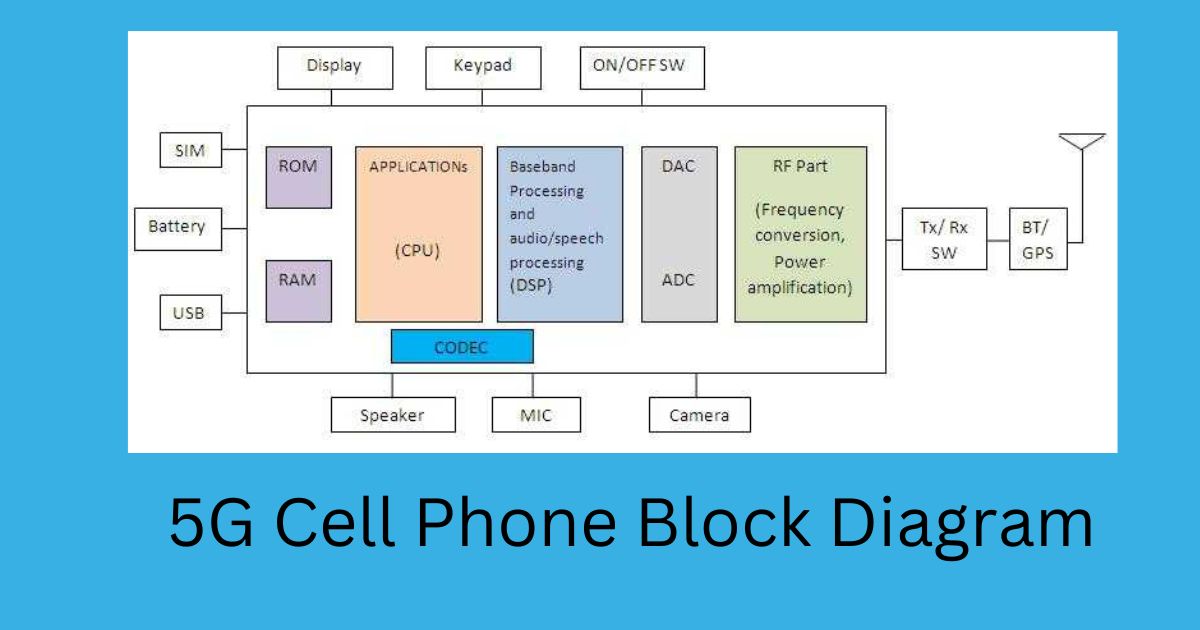
Its additional features are layered edge computing, enhanced common public radio interface, and beamforming. In 5G, network management is expected to be software-based, with network functions & resources virtualized on Edges & Cores. With network functions built using Microservices methodologies, a Service-based architecture for 5G would eventually develop to an end-to-end Service Mesh, featuring Service Discovery, Load Balancing, Encryption, Authentication, and Authorization, while employing a Sidecar to communicate between services.
The service-based architecture in the core 5G standalone (SA) allows Telcos to scale networks and services more effectively, increase resiliency, and unlock new capabilities to support the countless needs of enterprises and end users migrating to 5G. The service-based architecture of the 5G core replaces a more monolithic EPC with network functions that can run independently from each other and are not dependent on hardware, which gives telcos greater freedom over what vendors and hardware they choose to use. Services are essential building blocks used for creating and running mobile network functions. These include slice management, network data analytics, functions, and the signaling core 5G.
Conclusion On 5G
The conclusion emphasizes that the 5G networks will be a crucial infrastructure to support the maintenance of important social and economic functions. The report notes the opportunities for DHS and other national security enterprise organizations include new and improved capabilities supported by 5G and 6G network infrastructures, which will allow the extension of connected devices and realization of the Internet of Things (IoT) at a mass scale.
Continued evolution of 5G technologies and identification of next-generation 6G network technologies will present a number of opportunities for improving Homeland Securitys and homeland security enterprises mission capabilities, along with associated risks and uncertainties, that must be addressed. The 5G network and the IoT that it will enable will dramatically increase the number of wireless devices over current circumstances, requiring increased infrastructure densities. Furthermore, the wide spread population distributions and large geographical footprints of countries will also pose challenges with regards to the implementation of an adequate infrastructure for a new 5G network.
There are also certain technological challenges, such as more bands needed at higher frequencies, shorter range operation 5G antennas, which would mean higher costs of infrastructure, making the 5G technology less viable as a forthcoming service. Upgrading to 5G networking technologies would enable saving a lot of money on power costs and maintenance since it would smartly manage energy usage and traffic flows, among others.
This will help businesses accommodate a huge amount of equipment within their networking infrastructure, and maintain large numbers of connections between people and devices within reduced space. Network slicing would allow wireless network connections to be tailored for particular uses or business cases, and can be sold as an As-a-Service. Overall, 5th Generation Wireless (5G) is expected to create various new applications, uses, and business cases as the technology is deployed.
The 5G network will operate in multiple different frequency bands , of which lower frequencies are proposed for phase one of a 5G network. This cloud-native network will make it easier for developers to build new 5G applications. AWS believes that this approach for 5G deployments will enable digital service providers (DSPs) to take advantage of the benefits of the cloud native network.
The higher speeds and significant increases in throughput offered by the proposed new network make possible the use of Digitally Assisted Virtual Surgery (DAV), i.e. While some researchers and analysts have suggested that existing 4G long-term evolution (LTE) technologies are adequate for most IoT use cases, this article contends that only a high-speed, high-capacity, low-latency 5G broadband network would satisfy the demands from increasingly data-intensive applications.
High-speed, next-generation broadband networks and IoT, together with the technologies and applications high speeds would enable, can significantly benefit people of color and position them to take advantage of emerging pathways for economic and social opportunity. It is also argued that adding very high numbers of 5G network components would increase the overall EMF exposure to the environment, and high EMF exposure could result in negative health effects.